Difference between revisions of "West Florida"
Ultraking101 (talk | contribs) |
Ultraking101 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
The Spanish opted to resettle Pensacola in November 1698 as a buffer against French settlements in Louisiana and Mobile. However, in May 1719 Spain would lose Pensacola during the War of the Quadruple Alliance, when French forces led by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville took and occupied the settlement until a larger Spanish force came in August 1719 to recover the settlement, only to then be recaptured by France the following month in September 1719. In 1720 the war concluded, and the Pensacola territory was returned to Spain, although France did not retreat until 1726 back to its forts in Mobile and Biloxi further west. | The Spanish opted to resettle Pensacola in November 1698 as a buffer against French settlements in Louisiana and Mobile. However, in May 1719 Spain would lose Pensacola during the War of the Quadruple Alliance, when French forces led by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville took and occupied the settlement until a larger Spanish force came in August 1719 to recover the settlement, only to then be recaptured by France the following month in September 1719. In 1720 the war concluded, and the Pensacola territory was returned to Spain, although France did not retreat until 1726 back to its forts in Mobile and Biloxi further west. | ||
| − | After the French retreated from Pensacola, the city was rebuilt, but was ravaged by hurricanes in 1752 and 1761. However, in 1763 as part of | + | After the French retreated from Pensacola, the city was rebuilt, but was ravaged by hurricanes in 1752 and 1761. However, in 1763 as part of Spanish concessions in the {{wpl|Treaty of Paris (1763)}} the the British took control of all Spanish colonial possession east of the Mississippi River, including all of West Florida ending Spanish rule in the region. |
===== Louisiana (New France) (1703–1763)===== | ===== Louisiana (New France) (1703–1763)===== | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 21 December 2023
| Republic of West Florida | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
|
Anthem: God Bless the Sun | |
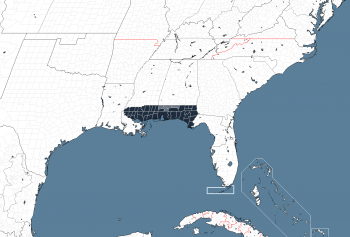 Location of West Florida (dark blue) | |
| Capital | Pensacola |
| Official languages | English |
| Recognised national languages | Spanish, French Creole |
| Demonym | West Floridian |
| Government | Federal Presidential Constitutional Republic |
• President | Janine Davidson |
• Vice-President | Sam Jones |
• House Speaker | Phil Ehr |
• Chief Justice | Tom Parker |
| Establishment | |
• Gulf Coast Defense Region | March 1993 – November 18, 1995 |
• Christmas Court Ruling | December 27, 1993 |
• Alabama and Mississippi Governments Dissolved | August 1994 |
• Independence | December 3rd, 1995 (As part of the Treaty of Washington) |
• Founding of the House and Senate | March 5, 1996 |
• Current Constitution | July 5, 2007 |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | 7,110,617 (102nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $339,040 USD |
• Per capita | $64,403 (13th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $347.4 Billion |
• Per capita | $56,910 |
| Gini (2020) |
31.4 medium |
| HDI (2022) |
0.895 very high |
| Currency | Dollar ($) |
| Time zone | CST (UTC-6) |
| Date format | mm-dd-yyyy |
| Drives on the | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | WFR |
| Internet TLD | .wf |
West Florida, officially known as the Republic of West Florida is a Federal presidential constitutional republic along the Gulf Coast of the former United States of America. The government is derived from the various military bases in the region forming a defense league between them to preserve some basis of American Government in the South of the USA. The region was effectively ruled by a military council with a puppet president. The government is still highly dependent on the military for general national support as much of the national population was once military or former military population. West Florida is the lone stabilized nation in the deep south with the rest controlled by various terrorist groups in the region now known as "New Afrika".
Etymology
The first documentary evidence of the phrase "West Florida" dates back to the British colonial era in the Royal Proclamation of 1763, with West Florida and East Florida, separated by the Apalachicola River. The term "West Florida" is derived by Spanish translation "Florida Occidental", itself derived from the Spanish conqueror and explorer Juan Ponce de León's name for the region "Florida" meaning "full of flowers".
West Florida derived the name "Republic of West Florida" from the short-lived 1810 revolution in the region against colonial Spanish rulers in an attempt to create a independent democratic republic. In 1994 the Gulf Coast Defense Force reorganized using the old name for the region from the old revolutionary forces.
History
Colonial Era
First Spanish rule (1513–1763)
The first European exploration of the area began in the 16th century with Diego Miruelo may have been the first European to sail into Pensacola Bay in 1516. The first Spanish settlement expedition in the region was large at around 1,500 settlers, first settling in Pensacola on August 15, 1559. Weeks later, a hurricane would destroyed many of the settlements, with settlers surviving in Pensacola till 1561. Pensacola would officially be the first multi-year European settlement in the territory of what is the United States. Although the Spanish later concluded that northwest Florida was too dangerous to settle for the time period and abandoned efforts to colonize the region for 137 years.
The Spanish opted to resettle Pensacola in November 1698 as a buffer against French settlements in Louisiana and Mobile. However, in May 1719 Spain would lose Pensacola during the War of the Quadruple Alliance, when French forces led by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville took and occupied the settlement until a larger Spanish force came in August 1719 to recover the settlement, only to then be recaptured by France the following month in September 1719. In 1720 the war concluded, and the Pensacola territory was returned to Spain, although France did not retreat until 1726 back to its forts in Mobile and Biloxi further west.
After the French retreated from Pensacola, the city was rebuilt, but was ravaged by hurricanes in 1752 and 1761. However, in 1763 as part of Spanish concessions in the Treaty of Paris (1763) the the British took control of all Spanish colonial possession east of the Mississippi River, including all of West Florida ending Spanish rule in the region.
Louisiana (New France) (1703–1763)
In 1699, French colonists established the formed the first permanent European settlement in French Louisiana, at Fort Maurepas near present-day Pascagoula. However, in 1702 French Settlers opted to constructed Fort Louis de la Louisiane further east on the Mobile River in order to protect France's claims to the La Louisiane region, with the settlement La Mobile becoming the capital of La Louisiane.
In May 1719, Spain would lose Pensacola during the War of the Quadruple Alliance, when French forces led by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville marched eastward to capture the settlement of Pensacola. The French maintained their hold on the settlement until a larger Spanish force came in August 1719 to recover their lost territory, only to then be recaptured by the French Navy the following month in September 1719. In 1720 the war concluded, and the Pensacola territory was returned to Spain, although France did not retreat until 1726 back to its forts in Mobile and Biloxi further west.
In 1720, the current location of Biloxi was settled for the first time around Fort Louis. Similarly in during the same year, the French opted to change the administrative capital of La Louisiane from La Mobile (Mobile) to Bilocci (Biloxi).
In 1763 as part of French concessions in the Treaty of Paris (1763) the the British took control of all French colonial possession east of the Mississippi River, including the settlement of La Mobile and Bilocci, being renamed to Mobile and Biloxi by the British.
British West Florida (1763-1783)
Second Spanish rule (1783-1821)
Republic of West Florida (1810)
American Territory and Statehood
American Civil War (1861-1865)
Early 20th Century
Cold War
Collapse of America & Independence (1993-1996)
Collapse of America
Independence
21st Century
Hurricane Katrina
Miracle Decade
Geography
Government and Politics
Administrative divisions
Military
Nuclear Policy
West Florida is not confirmed to be in the possession of weapons of mass destruction, and has not ratified the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). The Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) has argued that West Florida is in possession of undeclared chemical warfare capabilities and a biological warfare program.[2] Officially, West Florida neither confirms nor denies possessing nuclear weapons.
